Day Trading vs Swing Trading – Choosing the Right Style
In the dynamic world of financial markets, adopting a trading style that resonates with your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and lifestyle is paramount to achieving success. Among the myriad of strategies employed by traders, day trading and swing trading stand out as two of the most popular and distinct approaches. Each style offers a unique set of advantages and challenges, tailored to fit different types of traders—from the fast-paced, decisive day trader to the patient, analytical swing trader. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of day trading versus swing trading, providing a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed decision on which style best aligns with your trading goals and personal preferences. By understanding the key characteristics, risks, and rewards associated with each approach, you can navigate the forex market, stocks, crypto, etc., with greater confidence and precision, crafting a trading path that is uniquely yours.
Understanding Day Trading
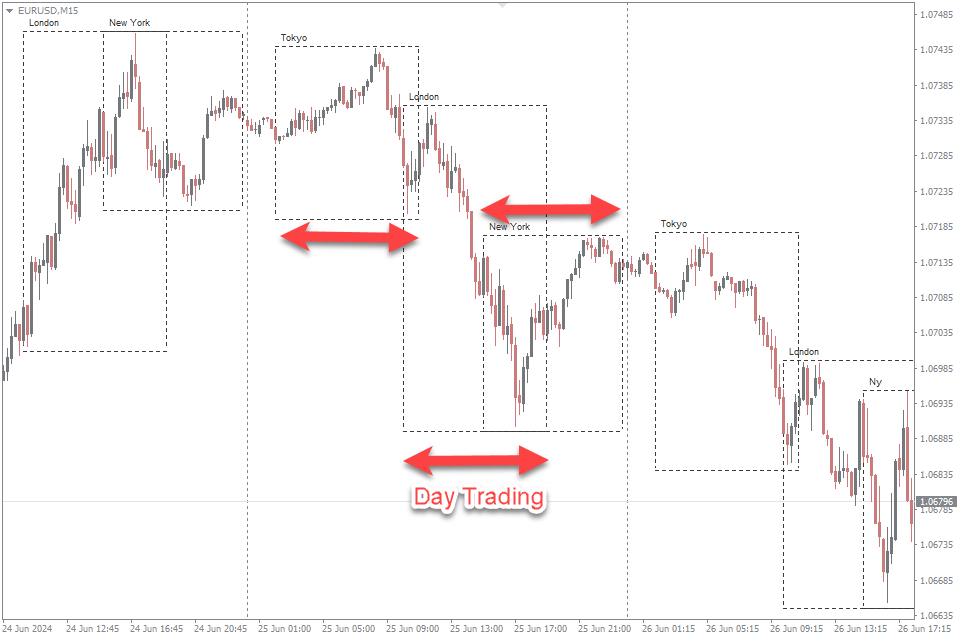
Day trading, a high-octane trading strategy, captivates those seeking to capitalize on the financial markets’ daily volatility. Characterized by its fast-paced nature, day trading involves executing multiple trades within the same trading day during a trading session, aiming to exploit short-term price movements for profit. This approach demands a deep understanding of market trends, technical analysis, and the ability to make quick, informed decisions.
The key elements of day trading that trader need to focus on include:
Technical Analysis – Mastery of chart patterns, indicators, and technical tools is essential for identifying short-term price movements and making informed trading decisions.
Risk Management – Implementing strict money management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and managing position sizes, is crucial to protect against significant losses.
Market Volatility and Liquidity – Day traders should focus on highly volatility liquidity markets or securities that offer enough price movement to make profits within a single trading day.
Discipline – Sticking to a well-defined trading plan and resisting emotional trading decisions are vital for consistency and long-term success in day trading.
Speed and Efficiency – The ability to quickly execute trades is critical in taking advantage of short-term opportunities. This often requires reliable trading platforms and real-time market data.
Continuous Learning – The market is always evolving, so staying informed about financial news, market trends, and trading techniques is necessary for adapting strategies.
Leverage – Understanding how to use leverage effectively can amplify gains but also increases the risk, so it’s important to use it wisely.
Time Commitment – Day trading requires a significant time investment, as traders need to monitor the markets and manage trades throughout the trading session. By focusing on these elements, day traders can enhance their trading performance and navigate the fast-paced environment of day trading more effectively.
Exploring Swing Trading
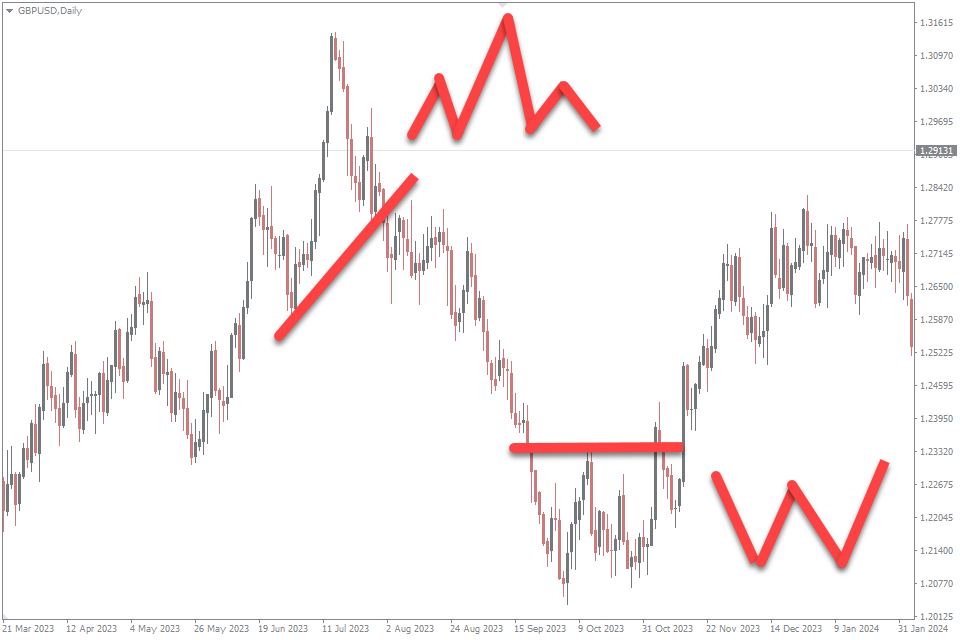
Swing trading stands as a strategic beacon for traders aiming to harness the momentum of financial markets over a medium-term horizon, typically spanning several days to weeks. This trading style is distinguished by its analytical depth, where traders leverage technical and fundamental analysis to pinpoint potential market movements and execute trades that capture the essence of price swings. Unlike the rapid-fire nature of day trading, swing trading offers a balanced tempo, allowing traders to thoughtfully analyze trendline and make calculated decisions without the pressure of intraday volatility. Key to swing trading is the identification of ‘swing points’—moments where market momentum is poised to shift—enabling traders to enter and exit positions at the most opportune times. This approach requires patience, a keen eye for market sentiment, and a robust understanding of risk management to mitigate potential downturns and maximize returns. Swing traders often benefit from the reduced time commitment compared to day trading, making it an appealing option for those with other commitments or who prefer a less intensive trading experience. Swing traders employ a variety of key strategies to identify potential market movements and maximize returns, focusing on capturing price swings within a medium-term timeframe. Some of these strategies include:
Trend Analysis – Swing traders often use trend lines, moving averages, and other indicators to identify the overall direction of the market or a specific asset. Trading in the direction of the trend increases the chances of successful trades.
Support and Resistance Levels – Identifying key support and resistance levels helps swing traders determine potential entry and exit points, as these levels often indicate where price movements may pause or reverse.
Technical Indicators – Tools such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Stochastic Oscillator are used to assess market conditions, identify overbought or oversold areas, and predict potential reversals.
Candlestick Charts Patterns – Swing traders analyze chart patterns like head and shoulders, flags, and triangles to predict future price action based on historical patterns.
Volume Analysis – Analyzing trading volume can provide insights into the strength of a price movement. An increase in volume often accompanies significant price changes, indicating strong buyer or seller interest.
Fibonacci Retracements – This tool is used to identify potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence, helping traders find strategic entry and exit points during retracements in a trend.
Risk Management – Establishing clear risk-reward ratio rules, including setting stop-loss order and take-profit order, and determining position sizes based on the trader’s risk tolerance, is crucial to protect profits and limit losses.
Fundamental Analysis – Although less common in swing trading than in long-term investment strategies, some swing traders incorporate fundamental analysis to identify undervalued or overvalued assets that may experience price corrections.
Comparing Risk and Reward
When juxtaposing the risk and reward profiles of day trading versus swing trading, it becomes evident that each strategy carves out its distinct niche within the spectrum of financial market endeavors. Day trading, characterized by its fast-paced, high-frequency trades within a single market day, inherently embraces a higher risk threshold due to its exposure to intraday market volatility and the amplified use of leverage. This approach demands acute market savvy, rapid decision-making, and an unwavering discipline to mitigate potential losses, yet it tantalizes with the promise of immediate, substantial rewards for those who master its intricacies. Conversely, swing trading adopts a more measured pace, extending over days to weeks, which allows for a more thorough analysis and a tempered exposure to market fluctuations. While swing trading reduces the risk of sudden market reversals inherent in shorter time frames, it introduces the challenge of overnight and weekend market gaps. Nonetheless, it offers the allure of significant returns through strategic, well-timed entries and exits in alignment with medium-term market trends.
Day trading and swing trading differ significantly in their risk and reward profiles due to their distinct operational time frames and trading tactics:
Risk Exposure
Day Trading: Involves higher risk exposure on a per-trade basis due to the use of leverage and the necessity to make quick decisions within the short intraday time frame. The rapid fluctuations of the market require constant monitoring and quick reactions to limit losses.
Swing Trading: Generally, involves lower risk exposure per trade as positions are held over a longer period, allowing traders to weather short-term volatility. However, swing traders are exposed to overnight and weekend market risks, which can introduce unexpected price gaps.
Reward Potential
Day Trading: Offers the potential for quick profits due to the high volume of trades. Successful day traders can capitalize on small price movements, compounding gains over multiple trades within a day.
Swing Trading: Rewards come from capturing larger price movements over days or weeks. While profits may accrue more slowly, the gains from a single swing trade can be substantial if the market moves favorably.
Market Volatility
Day Trading: High market volatility can both increase risk and reward, as price swings are more pronounced and occur rapidly, offering more opportunities but also greater chances of loss.
Swing Trading: Swing traders must also navigate volatility but can plan their trades around it, using it to their advantage to enter trades at more favorable prices.
Capital Utilization
Day Trading: Requires a higher capital allocation for each trade to make meaningful profits from small price changes, often necessitating a larger trading account.
Swing Trading: Can be done with less capital per trade as profits are derived from larger price swings over a longer timeframe.
Timeframe and Analysis
Day Trading: Short-term timeframe necessitates a focus on technical analysis and quick interpretation of market data.
Swing Trading: Longer-term positions allow for a more balanced approach, incorporating both technical and fundamental analysis to inform trade decisions.
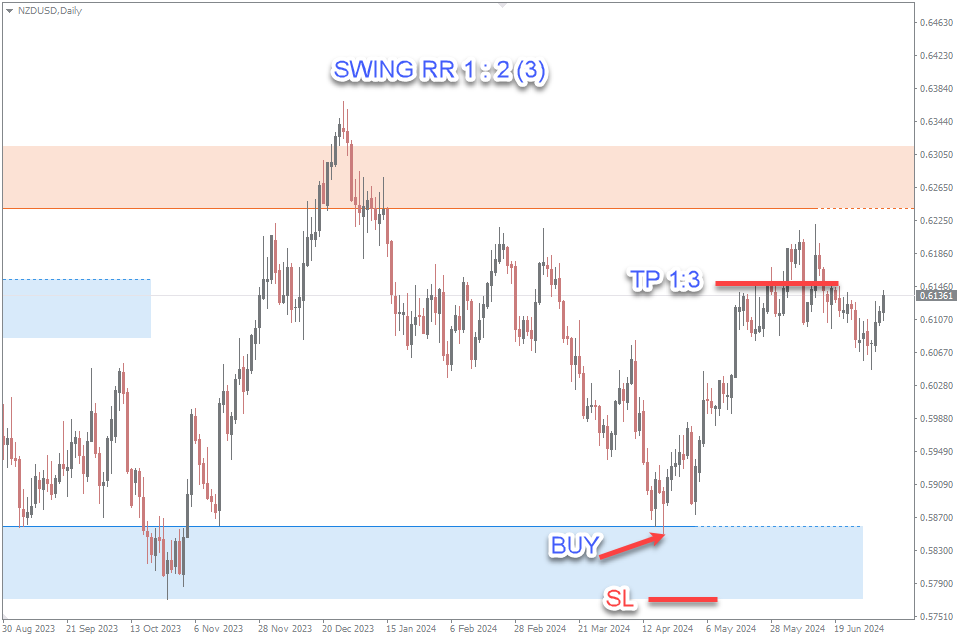
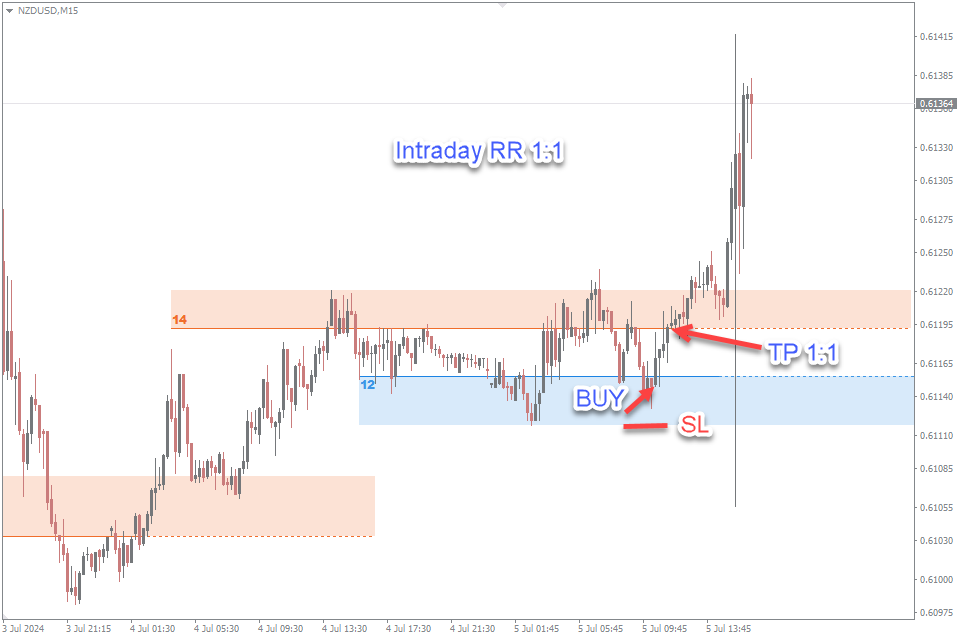
Understanding the differences in risk-reward ratios between intraday and swing trading is essential for developing a successful trading strategy. While intraday trading focuses on numerous small gains with a 1:1 risk-reward ratio, swing trading targets more significant profits with a 1:2 or 1:3 risk-reward ratio. By aligning their trading approach with their risk tolerance and market analysis skills, traders can enhance their chances of achieving consistent success in the forex market.
Time Commitment and Lifestyle Consideration
The divergence in time commitment and lifestyle considerations between day trading and swing trading is a pivotal factor that can greatly influence a trader’s decision in selecting the style that best complements their daily routine and personal preferences. Day trading demands an extensive time investment, requiring traders to remain tethered to their screens, vigilantly monitoring the markets during trading hours to capitalize on fleeting intraday opportunities. This high level of engagement suits individuals who can dedicate full-time hours to trading, thriving on the adrenaline of rapid decision-making and immediate results. On the contrary, swing trading offers a more flexible approach, accommodating those with other commitments, such as a full-time job or personal obligations. As swing trades unfold over days to weeks, this style permits a more relaxed pace, allowing traders to conduct market analysis, set up trades, and adjust positions outside of standard market hours. This reduced time requirement does not only cater to part-time traders but also to those seeking to balance trading with a lifestyle that values time for other pursuits. Ultimately, the choice between day trading and swing trading extends beyond mere strategy preference, touching upon the trader’s availability, lifestyle aspirations, and how they wish to integrate trading into their broader life context.
Capital Requirements
The capital requirements for day trading versus swing trading present a crucial consideration that significantly influences a trader’s approach and potential market engagement. Day trading, with its swift, short-term trades, often necessitates a higher initial capital investment due to regulatory stipulations and the need for sufficient leverage to capitalize on minimal price movements. In the United States, for instance, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) mandates a minimum of $25,000 in a trader’s account to day trade actively and frequently. This requirement underscores the need for substantial liquidity to manage and mitigate the risks associated with the high volume of trades and the potential rapid fluctuations in account value. If a trader’s account falls below this minimum equity requirement, they will not be allowed to day trade until the account is restored to the $25,000 minimum equity level. Conversely, swing trading, characterized by fewer transactions over longer periods, typically requires a lower capital threshold, making it more accessible to individuals with limited resources. The ability to leverage smaller capital for potentially significant gains over several days or weeks allows swing traders to effectively participate in the markets without the stringent capital demands of day trading. This distinction in capital requirements not only affects the feasibility of engaging in either trading style but also impacts the strategic planning and risk management approaches a trader must consider. Ultimately, understanding the capital implications of each trading style is essential for aligning one’s financial resources with their trading objectives, risk tolerance, and overall market strategy.
Trading Psychology Aspects
Navigating the psychological terrain of trading is as crucial as mastering technical strategies, with the mental and emotional demands of day trading and swing trading diverging significantly due to their distinct operational dynamics. Day trading, with its frenetic pace and high-stakes environment, requires a psychological resilience that can withstand the stress of rapid decision-making and the emotional rollercoaster of frequent gains and losses. This high-pressure setting demands an exceptional level of discipline, focus, and emotional detachment to prevent impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. In contrast, swing trading, with its extended timeframe, introduces a different psychological challenge: the test of patience and long-term vision. Swing traders must cultivate the ability to maintain a strategic outlook, resisting the urge to react hastily to short-term market fluctuations and instead staying the course until their trading thesis unfolds. This style also tests one’s tolerance for holding long position or short position through market volatility, requiring confidence in one’s analysis and the mental fortitude to weather potential downturns. Both trading styles necessitate a keen awareness of one’s emotional triggers and the development of strategies to mitigate their impact, emphasizing the critical role of psychology in trading success. Whether navigating the swift currents of day trading or the strategic depths of swing trading, the trader’s psychological resilience and emotional intelligence become pivotal in turning market challenges into opportunities.
Tools and Resources
In the realm of financial trading, equipping oneself with the right tools and resources is paramount for navigating the complexities of the market, whether one opts for the brisk pace of day trading or the deliberate approach of swing trading. For day traders, real-time data feeds, advanced charting software, and direct-access trading platform are indispensable for executing swift, informed trades. These traders rely heavily on technical analysis tools, such as momentum indicators and oscillators, to identify short-term price trend and entry/exit points within the day’s trading sessions (Asia, London, New York). Additionally, access to comprehensive news services and economic calendar is critical for staying abreast of market-moving events that can influence intraday trading strategies. On the other hand, swing traders benefit from a mix of technical and fundamental analysis tools that help in identifying medium-term market trends and potential swing points. Swing trading strategies often incorporate trading software that offers historical data analysis, enabling traders to study long-term price patterns and support and resistance zones. Both trading styles also leverage educational resources, including webinars, online courses, and trading forums, to continually refine strategies and adapt to changing market conditions. Moreover, risk management tools, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing calculators, are essential across both trading disciplines, ensuring traders can effectively manage their exposure and safeguard their capital. Ultimately, the judicious selection and application of these tools and resources can significantly influence a trader’s ability to make informed decisions, manage risks, and capitalize on market opportunities, aligning with their chosen trading style and objectives.
Making the Choice
Traders can determine which trading style best aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance through a series of introspective evaluations and practical considerations.
Here are steps and factors to consider in making this crucial decision:
Assess Financial Goals – Clearly define what you aim to achieve through trading. Are you looking for quick, daily profits or are you more interested in capturing larger gains over a longer period? Your financial objectives will heavily influence whether day trading or swing trading is more suitable.
Evaluate Risk Tolerance – Understand your capacity for risk. Day trading often involves higher risk due to rapid market fluctuations and the use of leverage, requiring a higher risk tolerance. Swing trading, while still risky, generally allows for more calculated risks over a longer timeframe.
Consider Time Availability – Reflect on the amount of time you can dedicate to trading. Day trading demands significant time investment, as it requires monitoring the markets and making quick decisions during trading hours. Swing trading can be more flexible, allowing for research and trading decisions to be made outside of standard market hours.
Analyze Market Knowledge and Skills – Assess your understanding of market analysis techniques. Day trading often relies heavily on technical analysis and real-time data interpretation, while swing trading can benefit from a combination of technical and fundamental analysis over a longer period.
Trial and Error – Experiment with both trading styles using simulation trading platforms or by allocating a small portion of your capital to each style. This practical experience can provide valuable insights into which style suits your personality, skills, and financial goals.
Risk Management Strategies – Consider which risk management strategies you are more comfortable with. Effective risk management is crucial in both styles, but the specific strategies may differ due to the differing time frames and goals.
Lifestyle Compatibility – Think about how trading fits into your overall lifestyle. Day trading may offer excitement and faster results but can also be more stressful and time-consuming. Swing trading may be better suited for those with other commitments or who prefer a less intense trading experience.
Educational Resources and Tools – Identify the resources and tools you have at your disposal. Both trading styles require access to specific types of information and technology, so consider which set of tools you’re more prepared to invest in. By carefully considering these factors, traders can make a more informed decision about which trading style better suits their individual preferences, goals, and risk tolerance, setting the stage for a more tailored and potentially rewarding trading journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision between day trading and swing trading hinges on a harmonious alignment of one’s financial aspirations, risk tolerance, lifestyle, and the commitment one is willing to make to the markets. Day trading, with its rapid-fire nature, suits those who revel in the adrenaline of the trading floor and possess the acumen to navigate the tumultuous waves of the market within the confines of a single day. Swing trading, in contrast, appeals to the strategic thinker, the individual who takes a measured approach to capture gains over a longer arc, balancing market analysis with patience. Both styles offer distinct pathways to potential profitability but require a deep understanding of market mechanics, a steadfast adherence to risk management, and an unyielding discipline to succeed. As traders carve their niches in the financial landscape, the choice of trading style becomes a reflection of their personal trading philosophy and a testament to their adaptability in the face of the market’s ever-evolving nature. Whether through the swift currents of day trading or the strategic depths of swing trading, success is not dictated by the style chosen but by how well one can wield their chosen strategy to navigate the complex market environment.



















Leave a Reply