Scalping vs Swing Trading: Which Strategy Suits You Best?
Navigating the world of trading can be daunting, especially when choosing between scalping and swing trading. Scalping is a fast-paced strategy where traders make numerous trades within minutes or even seconds, aiming to profit from small price fluctuations. In contrast, swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks to capitalize on more significant price movements. Each approach has its own set of benefits and challenges, making it crucial to understand which strategy aligns with your trading style, risk tolerance, and financial goals. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of scalping and swing trading, providing insights into which strategy may best suit your trading style.
What is Scalping?
Scalping is a fast-paced trading strategy designed for those who thrive on quick decision-making and rapid market movements. This approach involves executing numerous trades within a single trading day to profit from small price fluctuations. Scalpers often hold positions for just a few seconds to a few minutes, aiming to accumulate small gains that can add up over time. Utilizing high leverage and tight stop-loss orders, scalping demands a deep understanding of market dynamics, impeccable timing, and robust technical analysis skills. Tools like candlestick charts, moving averages, and volume indicators are crucial for identifying short-term opportunities in the forex market, particularly in high-volatility currency pairs. Scalping is best suited for traders who can dedicate substantial time to monitoring the markets, have a high tolerance for stress, and can implement a disciplined risk management strategies to maximize their risk-reward ratio.
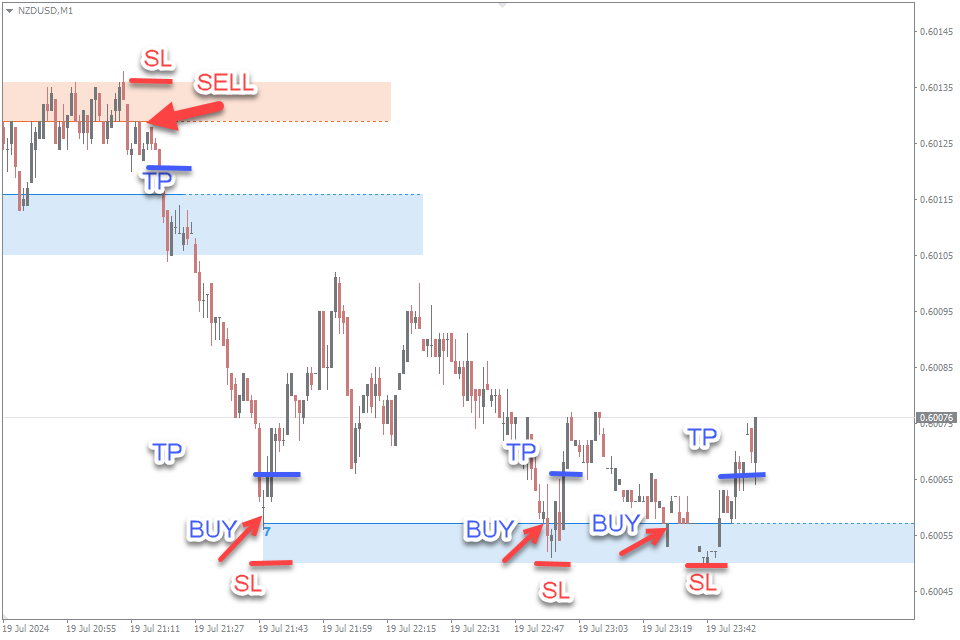
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a popular trading strategy that caters to those who prefer a more relaxed yet strategic approach to the forex market, stock or crypto. Unlike scalping, which focuses on minute-to-minute price changes, swing trading aims to capture larger price moves over several days to weeks. This strategy involves holding positions for longer periods, allowing traders to take advantage of significant market trends and reversals. Swing traders rely heavily on technical analysis tools such as moving averages, RSI, MACD, and candlestick patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Fundamental analysis also plays a crucial role in swing trading, as economic indicators and economic calendar, news events, and market sentiment can significantly impact price trends. This method is ideal for traders who cannot monitor the markets continuously but still want to capitalize on medium-term market movements.
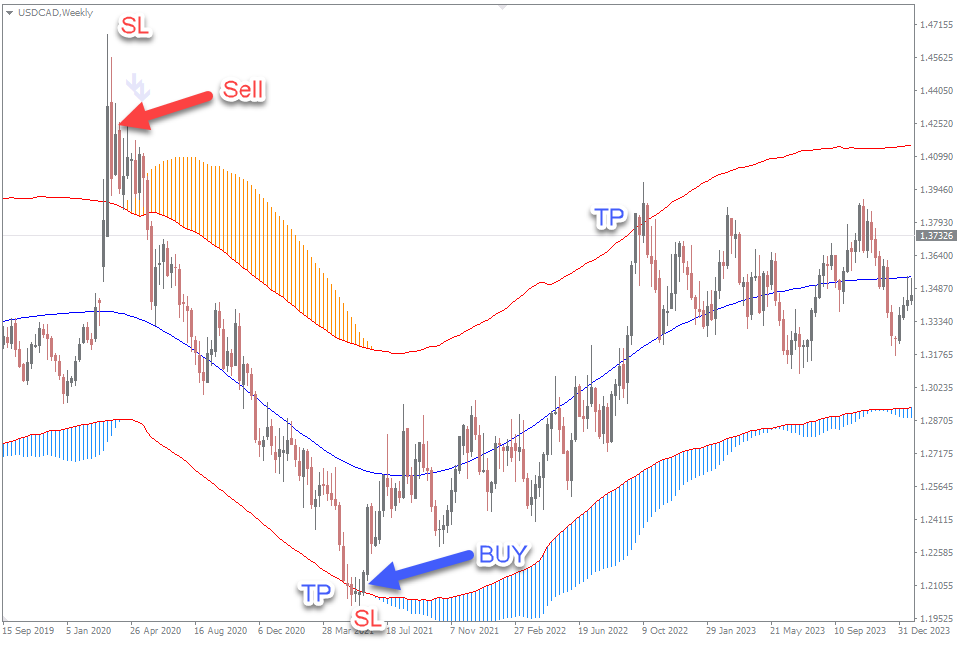
Risk and Reward
In the debate of scalping vs. swing trading, understanding the risk and reward dynamics is crucial to determining which strategy suits you best. Scalping involves executing a high volume of trades within a short period, typically aiming for small profit margins on each trade. This high-frequency trading approach inherently carries a higher risk, as even minor price fluctuations can significantly impact the outcome. Scalpers must be adept at managing these risks, often using tight stop-loss orders and rigorous money management techniques to mitigate potential losses. The reward in scalping comes from the cumulative effect of multiple small gains, which can add up to substantial profits over time if executed correctly. The risk-reward ratio in scalping trading is typically is less favorable, leading to 0.9- 0.5.
Conversely, swing trading is designed to capture larger price movements over several days to weeks. This strategy generally involves holding positions for a longer duration, which can expose traders to overnight market risks and potential gaps in price. However, the risk-reward ratio in swing trading is typically more favorable, often aiming for a 1:2 or even 1:3 ratio. This means that the potential reward is two to three times the risk taken on each trade. Swing traders utilize comprehensive technical analysis, focusing on chart patterns and price trends to identify optimal entry and exit points, while also incorporating fundamental analysis to understand market conditions.
Both scalping and swing trading come with their own set of risks and rewards. Scalping demands a high level of discipline and quick reflexes to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities, while swing trading requires patience and a strategic outlook to ride out longer-term trends.
Time Commitment
When choosing between scalping and swing trading, understanding the time commitment required for each strategy is essential. Scalping is a high-intensity trading approach that demands constant attention and quick decision-making. Scalpers typically spend several hours a day in front of their trading screens, analyzing real-time price movements, executing rapid trades, and closely monitoring market conditions. The fast-paced nature of scalping requires traders to stay highly focused and responsive to even the slightest market fluctuations, making it a full-time commitment for those who seek to maximize profits from this strategy. Due to the need for rapid execution and quick reactions, scalping is best suited for traders who can dedicate significant time and energy to their trading activities.
On the other hand, swing trading is less time-intensive, offering more flexibility for those with other commitments. Swing traders usually conduct thorough market analysis during off-hours, using technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points and setting up their trades based on expected price movements over the next several days to weeks. This approach allows swing traders to spend less time actively monitoring the markets throughout the trading day. Instead, they rely on their analysis and set stop-loss and take-profit orders to manage their trades automatically. While swing trading still requires regular review and adjustment of positions, it is generally less demanding than scalping in terms of continuous market engagement.
Ultimately, the time commitment for scalping vs. swing trading varies significantly. Scalping is ideal for traders who thrive in a fast-paced environment and can devote several hours each day to active trading. In contrast, swing trading is more suitable for those who prefer a balanced approach, allowing for a more flexible schedule and less intensive market monitoring. By aligning your trading strategy with your available time and lifestyle, you can optimize your trading performance and achieve your financial goals.
Technical Analysis
In the realms of scalping and swing trading, technical analysis plays a crucial role in formulating effective trading strategies. For scalpers, technical analysis is focused on very short-term price movements and patterns. Scalpers often use high-frequency chart patterns, such as candlestick formations, trend lines, and moving averages, to identify precise entry and exit points. Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands are frequently employed to gauge market conditions and execute rapid trades. Scalping demands real-time technical analysis to capitalize on minute price changes and maintain a competitive edge in high-volatility environments.
In contrast, swing trading relies on a more extended technical analysis approach. Swing traders analyze daily and weekly charts to identify medium-term price trends and potential reversal points. They utilize indicators such as Fibonacci retracement levels, moving averages, and momentum oscillators to assess market conditions and make informed decisions. Swing traders focus on chart patterns like head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, which help them forecast future price movements over several days or weeks. The emphasis is on understanding broader market trends and setting up trades that capture significant price swings.
Both strategies benefit from technical analysis, but the depth and duration of analysis differ. Scalping requires rapid and precise technical evaluation, whereas swing trading involves a more comprehensive and prolonged analysis of price trends and patterns.
Psychological Factors
When choosing between scalping and swing trading, understanding the psychological factors that influence each strategy is vital. Scalping demands intense focus and rapid decision-making, which can be mentally taxing. Traders need to stay alert and react swiftly to small price movements, which requires a high tolerance for stress and the ability to maintain composure under pressure. The fast-paced nature of scalping can lead to frequent trades and quick wins or losses, making it crucial for scalpers to have strong psychological resilience and disciplined emotional control to avoid impulsive decisions.
Swing trading, on the other hand, involves a longer time horizon, requiring patience and a different psychological approach. Swing traders must be prepared for longer periods of market exposure and potential fluctuations in their trades. This strategy necessitates the ability to endure market volatility and resist the urge to constantly check positions. Swing traders often face emotional challenges related to waiting for their trades to develop and maintaining conviction in their analysis despite short-term market movements. Effective swing traders balance their patience with strategic planning, focusing on medium-term trends and managing the emotional highs and lows of trading over days or weeks.
Both scalping and swing trading present unique trading psychology demands. Scalpers need to handle high-frequency trading pressure, while swing traders must cope with the psychological strain of holding positions for longer durations. By recognizing these psychological factors and developing coping strategies, traders can better align their mental fortitude with their chosen trading style, ultimately enhancing their trading performance
Market Conditions
When evaluating scalping vs. swing trading, market conditions play a pivotal role in determining which strategy is most effective. Scalping thrives in highly liquid markets with narrow spreads and high volatility liquidity. The ideal conditions for scalping include fast-moving markets where small price movements can be exploited for quick profits. Scalpers benefit from market environments with consistent volume and minimal slippage, as these factors contribute to more precise entry and exit points. Scalping strategies are well-suited to forex pairs with high liquidity, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY, where rapid transactions can be executed efficiently.
Conversely, swing traders look for market stability and clear trends to maximize profit potential from larger price swings. Swing traders look for opportunities over several days or weeks, relying on significant price movements to capture larger gains. Market conditions that favor swing trading include clear support and resistance zones, which help in identifying potential entry and exit points based on technical analysis. Swing traders also benefit from market conditions with moderate liquidity and trend strength, allowing them to hold positions over longer periods while avoiding excessive noise and short-term volatility.
Understanding and adapting to market conditions is crucial for both strategies. Scalpers need to navigate high-frequency trading environments with precision, while swing traders must focus on trend analysis and patience.
Trading Costs
When choosing between scalping and swing trading, understanding trading costs is essential, as these expenses can significantly impact overall profitability. Scalping involves executing numerous trades within short time frames, making transaction costs a critical factor. Scalpers typically incur higher costs due to the frequency of trades, including spread costs, commissions, and slippage. The frequent trading activity means that even small spreads or commissions can accumulate, potentially eroding profits. Therefore, choosing a trading platform with low transaction fees and tight spreads is crucial for scalpers to maintain profitability.
In contrast, swing trading generally involves fewer trades over a longer duration. This means lower cumulative transaction costs compared to scalping. Swing traders may still incur costs such as brokerage fees, overnight financing charges, and slippage, but these are spread across fewer transactions. The lower frequency of trades helps in managing costs more effectively and reduces the impact of fees on overall returns. Swing traders often focus on capturing larger price movements, which can offset the cost of trading commissions and market impact over the course of their trades.
In summary, trading costs are a significant consideration when deciding between scalping and swing trading. Scalping requires careful management of transaction fees due to its high-frequency nature, while swing trading benefits from a lower overall cost structure due to its less frequent trading activity.
Conclusion
When comparing scalping and swing trading, it’s crucial to understand the distinct characteristics and benefits of each strategy to make an informed decision about which method suits your trading style and goals. Scalping involves executing numerous trades within a single day, aiming to profit from small price movements. This approach demands quick decision-making, intense focus, and a high tolerance for trading costs due to the high frequency of trades. Scalpers must be adept at using real-time data and technical analysis tools, maintaining a high level of concentration, and managing numerous trades effectively. They thrive on market volatility and rapid price changes, leveraging their ability to react swiftly to fluctuations.
In contrast, swing trading focuses on capturing larger price movements over several days or weeks. This strategy results in fewer trades and generally lower trading costs, as traders aim to benefit from medium-term trends and price swings. Swing traders prioritize a more strategic and less time-intensive approach, analyzing chart patterns, trendlines, and fundamental factors to identify optimal entry and exit points. This method is well-suited for individuals who can dedicate a reasonable amount of time to market analysis but cannot commit to the constant vigilance required for scalping.
Ultimately, the choice between scalping and swing trading should align with your risk tolerance, time commitment, and psychological comfort. Consider factors such as market conditions, trading frequency, and technical skills when making your decision. By assessing these elements, you can determine which strategy best fits your trading style, financial goals, and overall market approach.
In conclusion, both scalping and swing trading offer unique advantages and challenges, making the choice between them highly personal. Scalping is suited for those who can manage high trading costs and thrive on frequent trading and rapid market movements. In contrast, swing trading appeals to traders who prefer a more measured approach, benefiting from lower trading costs and longer-term market trends. By carefully assessing your trading style, risk tolerance, and financial goals, you can determine whether scalping or swing trading is the best fit for your investment strategy. Embrace the strategy that complements your personal strengths and market insights, and adapt your trading plan to achieve your desired results in the dynamic world of trading.




















Comment (1)
hello
It is an interesting strategy. How can I get it? Please help. Thank you